“UN: Drastic Changes Needed 2 Avoid ‘Climate Hell'”
Introduction
The United Nations has issued a stark warning about the future of our planet, stating that “Climate Hell” is imminent unless drastic changes are made. UN Chief António Guterres emphasized the critical need for urgent action to address the accelerating climate crisis. His speech highlighted the catastrophic consequences of inaction and the necessity for immediate, transformative measures to mitigate climate change impacts.
Climate change refers to long-term alterations in temperature and weather patterns. These shifts can be natural, but since the 19th century, human activities have been the primary driver. The largest contributor to climate change is the burning of fossil fuels like coal, oil, and gas, which releases greenhouse gases (GHGs) such as carbon dioxide (CO2) into the atmosphere. These gases trap heat from the sun, causing the planet to warm—a phenomenon known as the greenhouse effect.
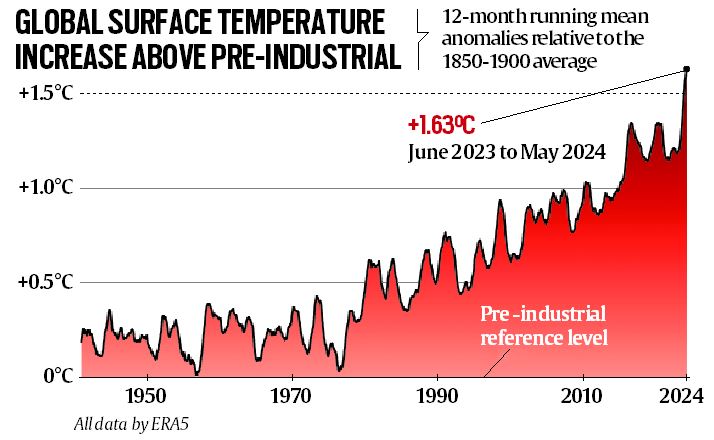
Scientific evidence overwhelmingly supports the reality of climate change. Observations show rising global temperatures, with the past decade being the warmest on record. Melting ice caps and glaciers, rising sea levels, and increasing frequency of extreme weather events serve as clear indicators. Recent natural disasters, such as wildfires in Australia, severe droughts, and devastating hurricanes in the Atlantic, underscore the urgent need for comprehensive climate action.
The impacts of climate change on natural systems are profound. Polar ice is melting, leading to rising sea levels, which threaten coastal communities. Ocean acidification, a result of increased CO2 absorption, affects marine life, particularly shellfish and coral reefs. Terrestrial ecosystems are also affected, with shifting habitats and the migration of species as they seek more favorable conditions. Biodiversity loss is accelerating, and the resilience of ecosystems is being compromised.
Climate change has significant implications for human health and the economy. Increased heatwaves lead to higher mortality rates, particularly among the elderly and vulnerable populations. The spread of diseases such as malaria and dengue fever is facilitated by changing climatic conditions. Economically, climate change affects agriculture through altered precipitation patterns and extreme weather, threatening food security. Infrastructure damage from severe weather events incurs high costs, and the displacement of communities leads to social and economic disruptions.
In his address, UN Chief António Guterres outlined a series of drastic changes necessary to combat the looming threat of climate catastrophe. He called for an immediate reduction in greenhouse gas emissions, a rapid transition to renewable energy sources, and significant investments in climate resilience. The proposed measures include both short-term actions, such as phasing out coal usage, and long-term strategies, like promoting sustainable agricultural practices.
The urgency and scale of required actions cannot be overstated. To limit global warming to 1.5 degrees Celsius above pre-industrial levels, as outlined in the Paris Agreement, global emissions need to be halved by 2030 and reach net zero by 2050. This requires an unprecedented transformation of energy, transport, and industrial systems. Guterres emphasized that the window of opportunity to avoid the worst impacts of climate change is rapidly closing.
Transition to Renewable Energy: A rapid shift to renewable energy sources, such as wind, solar, and hydroelectric power, is essential. This includes ending subsidies for fossil fuels and investing in renewable energy
infrastructure.
Climate Resilience Investments: Significant investments in climate resilience are necessary to protect communities from the impacts of climate change. This includes building resilient infrastructure, enhancing early warning systems, and supporting adaptation measures in vulnerable regions.
Phasing Out Coal: Phasing out coal, the most polluting fossil fuel, is a critical step. Guterres called for an end to new coal plant construction and a transition plan for existing coal plants.
Promoting Sustainable Practices: Long-term strategies include promoting sustainable agricultural practices, protecting forests, and restoring degraded ecosystems. These measures help sequester carbon and enhance biodiversity.
International agreements, such as the Paris Agreement, play a crucial role in guiding collective action. The Paris Agreement, adopted in 2015, aims to limit global warming to well below 2 degrees Celsius, with efforts to limit it to 1.5 degrees Celsius. It provides a framework for countries to set and achieve their climate targets, known as Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs).
Developed nations, responsible for the majority of historical emissions, have a significant responsibility to lead by example. They must reduce their carbon footprint and support developing countries in their transition to sustainable practices. This support includes financial assistance, technology transfer, and capacity-building initiatives. Developed countries have committed to mobilizing $100 billion annually by 2020 to help developing nations address climate change, a commitment that must be fulfilled and scaled up.
Conversely, developing nations face unique challenges in addressing climate change. These countries often have limited financial and technical resources, making it difficult to implement necessary measures. They also face pressing development needs, such as poverty alleviation and infrastructure development, which can conflict with climate goals. Financial and technological assistance from developed countries is crucial to help developing nations achieve their climate goals without compromising economic growth.
Achieving the ambitious goals set forth by the UN requires a coordinated global effort. Collaboration between governments, international organizations, the private sector, and civil society is essential. This includes sharing best practices, scaling up successful initiatives, and ensuring that all countries have access to the resources they need to transition to a sustainable future.
Read More: NASA-Roscosmos Team Launches Historic Journey To The ISS
The energy sector must undergo a fundamental transformation to reduce dependency on fossil fuels. Transitioning to renewable energy sources, such as wind, solar, and hydroelectric power, is essential. This involves significant investments in renewable energy infrastructure, ending subsidies for fossil fuels, and supporting research and development in new technologies. Energy efficiency measures, such as improving building insulation and adopting energy-efficient appliances, also play a crucial role.
The transportation sector needs a shift towards electric vehicles and sustainable public transport systems. This includes investing in electric vehicle infrastructure, such as charging stations, and providing incentives for the adoption of electric vehicles. Public transport systems should be expanded and modernized to reduce reliance on private cars. Promoting active transportation, such as walking and cycling, and supporting innovations in low-emission transportation technologies are also important strategies.
The agriculture and forestry sectors must adopt sustainable practices to reduce emissions and enhance carbon sequestration. Sustainable agricultural practices include precision farming, agroforestry, and the use of organic fertilizers. Protecting forests and restoring degraded ecosystems are critical for sequestering carbon and enhancing biodiversity. Initiatives such as reforestation and afforestation, as well as preventing deforestation, are essential components of climate action.
Industries need to implement green technologies to minimize their environmental impact. This includes adopting cleaner production processes, improving energy efficiency, and reducing waste. The circular economy model, which emphasizes recycling, reusing, and reducing waste, can significantly reduce industrial emissions. Investing in research and development to innovate and implement sustainable industrial practices is crucial for long-term sustainability.
Raising public awareness about climate change and promoting environmental education are critical components of the solution. Educating people about the causes and consequences of climate change, as well as the actions they can take, empowers individuals to contribute to climate solutions. Public campaigns, school curricula, and community engagement initiatives can all play a role in increasing awareness and fostering a culture of sustainability.
Understanding the economic implications of both action and inaction is vital. While transitioning to a sustainable economy entails upfront costs, the long-term benefits, including job creation in green industries and reduced healthcare costs, far outweigh these investments. The cost of inaction, including damage from extreme weather events, loss of biodiversity, and health impacts, is far greater than the cost of taking action now.
Political leaders must demonstrate the will to implement necessary policies and guide their nations toward a sustainable future. This includes enacting legislation to reduce emissions, supporting renewable energy projects, and investing in climate resilience. Political leaders must also engage with international climate negotiations, uphold commitments, and collaborate with other nations to address the global nature of the climate crisis.
Technological innovation plays a pivotal role in addressing climate change. Advancements in green technologies, such as carbon capture and storage, are essential for reducing emissions. Carbon capture and storage (CCS) technology captures CO2 emissions from sources like power plants and stores it underground to prevent it from entering the atmosphere. Continued investment in research and development is necessary to discover new solutions and improve existing technologies.
Promising areas of research include renewable energy storage, sustainable agriculture techniques, and climate-resilient infrastructure. Renewable energy storage technologies, such as advanced batteries, are critical for managing the intermittent nature of renewable energy sources like wind and solar. Sustainable agriculture techniques, such as precision farming and agroecology, can increase productivity while reducing environmental impact. Climate-resilient infrastructure, including flood defenses and drought-resistant crops, helps communities adapt to changing conditions.
Collaboration between the public and private sectors, as well as international cooperation, is essential to drive technological innovation. Public funding for research and development, along with private sector investment, can accelerate the development and deployment of new technologies. International collaboration allows countries to share knowledge, resources, and best practices, facilitating the global spread of innovative solutions.
Several countries and cities have successfully implemented climate solutions, providing valuable lessons for others. For instance, Denmark’s commitment to wind energy has significantly reduced its carbon emissions. Denmark has invested heavily in wind energy, making it a global leader in wind power production. The country has set ambitious targets for renewable energy and has implemented policies to support the development of wind farms, both onshore and offshore.
Costa Rica’s investment in renewable energy has made it a global leader in sustainability. The country generates nearly all of its electricity from renewable sources, primarily hydroelectric, wind, and geothermal energy. Costa Rica’s commitment to renewable energy, combined with its efforts to protect forests and biodiversity, has positioned it as a model for sustainable development.
Analyzing these successes and learning from less effective initiatives can guide future efforts and help avoid common pitfalls. For example, the transition to renewable energy requires careful planning and coordination to ensure a stable and reliable energy supply. Countries must also consider the social and economic impacts of transitioning away from fossil fuels, such as job losses in traditional energy sectors, and implement measures to support affected workers and communities.
To achieve the proposed changes, a detailed roadmap outlining specific milestones and targets is essential. This plan should include immediate actions, such as reducing emissions and increasing renewable energy capacity, and long-term goals, like achieving net-zero emissions by mid-century. The roadmap must be comprehensive, covering all sectors of the economy, and should be regularly updated to reflect new scientific insights and technological advancements.
Setting specific milestones and targets helps track progress and ensure accountability. These targets should be ambitious yet achievable, and should be based on the latest scientific evidence. Regular monitoring and reporting on progress are crucial for identifying areas where additional efforts are needed and for maintaining momentum.
Global collaboration and partnerships are crucial, involving governments, international organizations, the private sector, and civil society. This includes sharing knowledge and best practices, providing financial and technical support to developing countries, and fostering innovation through collaborative research and development efforts. International organizations, such as the UN and the World Bank, can play a key role in facilitating cooperation and coordinating global efforts.
While systemic changes are essential, individual actions also play a crucial role in addressing climate change. Individuals can reduce their carbon footprint by making sustainable choices in their daily lives, such as using energy-efficient appliances, reducing waste, and supporting renewable energy. Public pressure on governments and businesses to take climate action is also vital, as it can drive policy changes and corporate commitments to sustainability.
Conclusion
The UN’s call for drastic changes to avoid “Climate Hell” underscores the urgency of the climate crisis. The proposed measures, ranging from reducing emissions to promoting sustainable practices, require immediate and decisive action. It is imperative for nations, organizations, and individuals to collaborate and take responsibility for ensuring a sustainable future for all. Addressing climate change is not only an environmental imperative but also a moral and economic necessity. By taking bold and transformative actions now, we can secure a livable planet for current and future generatins.